With the FFT calculation in the module, it is assumed that the frequency spectrum and the resulting lines do not shift during the time it takes to calculate a data buffer. For shafts, this is only the case when they are running at a constant speed.
In the case of dynamic speed, narrow-band frequencies cannot be used to monitor or analyze damaged frequencies since these do not give valid results.
The following example shows the effect of variations in shaft speed on the resulting frequency spectrum during FFT calculation.
通过模块中的FFT计算,假设在计算数据缓冲区的时间内,频谱和其产生的谱线不会发生偏移,对于轴来说,只有当它们以恒定的速度运行时才会出现这种情况。
在动态速度的情况下,窄带频率不能用于监测或分析损坏的频率,因为这些频率不能给出有效的结果。
下面的例子显示了FFT计算过程中轴速度变化对所得频谱的影响。
Example
举例
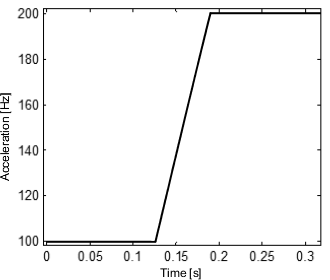
The speed of a shaft changes from 100 Hz to 200 Hz.
轴的速度从100Hz变化到200Hz。
|
|
Changing the speed of a shaft 轴速的变化 (在一个Buffer测量长度内,使用速度频率来模拟损坏。) |
|||
|
|
|
|||
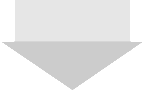
Fig.: Time signal 图: 时域信号 |
|
Change in the time signal 时域信号的变化 |
|||
|
|
|
|||
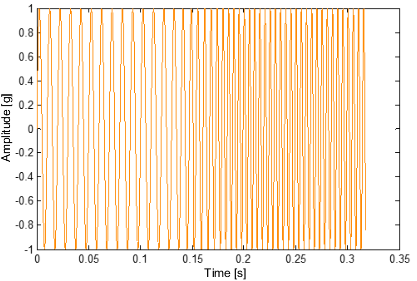
Fig.: Invalid result in the frequency spectrum 图: 频谱中的无效结果 |
|
Resulting spectrum 所得频谱 calculated from the time signal 根据时域信号计算 |
Possible approaches to measuring in a dynamic system
在动态系统中进行测量的可能的方法
•Best solution: Adopting separate measurements for trend analysis where the speed can be kept constant for the duration of measuring.
最佳解决方案: 采用单独的测量进行趋势分析,在测量期间速度可以保持恒定。
•If a measurement cannot be taken at constant speed, an assessment of the machine condition can be made using the characteristic values or a broadband frequency (in this example, this would be 80 to 220 Hz).
如果不能以恒定速度进行测量,则可以使用特征值或宽带频率(在本例中,这将是80至220 Hz)来评估机器状况。