X20CM4800X - Data sheet V1.04
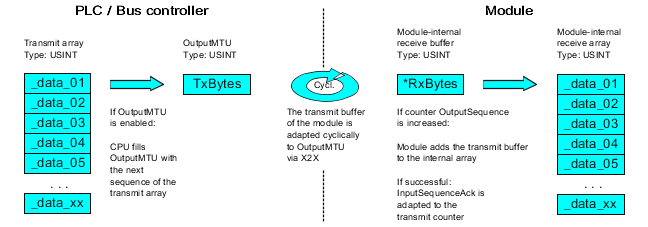
When transmitting data, the transmit array must be generated in the application program. Sequences are then transferred one by one using Flatstream and received by the module.
Information:
Although all B&R modules with Flatstream communication always support the most compact transfers in the output direction, it is recommended to use the same design for the transfer arrays in both communication directions.
Fig.: Flatstream communication (output)
Message smaller than OutputMTU
The length of the message is initially smaller than OutputMTU. In this case, one sequence would be sufficient to transfer the entire message and the necessary control byte.
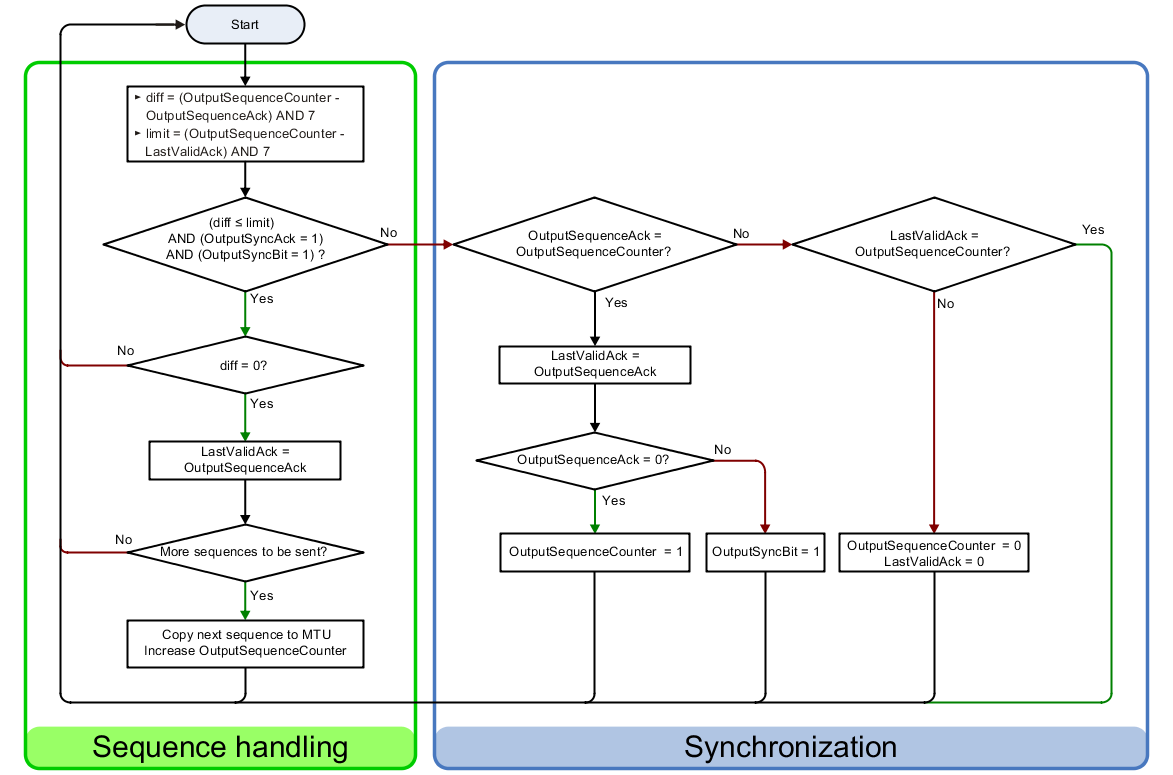
Algorithm
|
- The module monitors OutputSequenceCounter. |
0) Cyclic checks: - The CPU must check OutputSyncAck. → If OutputSyncAck = 0: Reset OutputSyncBit and resynchronize the channel. - The CPU must check whether OutputMTU is enabled. → If OutputSequenceCounter > InputSequenceAck: MTU is not enabled because the last sequence has not yet been acknowledged. |
1) Preparation (create transmit array): - The CPU must split up the message into valid segments and create the necessary control bytes. - The CPU must add the segments and control bytes to the transmit array. |
2) Transmit: - The CPU transfers the current element of the transmit array to OutputMTU. → The OutputMTU is transferred cyclically to the module's transmit buffer but not processed further. - The CPU must increase OutputSequenceCounter. |
Reaction: - The module accepts the bytes from the internal receive buffer and adds them to the internal receive array. - The module transmits acknowledgment and writes the value of OutputSequenceCounter to OutputSequenceAck. |
3) Completion: - The CPU must monitor OutputSequenceAck. → A sequence is only considered to have been transferred successfully if it has been acknowledged via OutputSequenceAck. In order to detect potential transfer errors in the last sequence as well, it is important to make sure that the length of the Completion phase is run through long enough.
Note: To monitor communication times exactly, the task cycles that have passed since the last increase of OutputSequenceCounter should be counted. In this way, the number of previous bus cycles necessary for the transfer can be measured. If the monitoring counter exceeds a predefined threshold, then the sequence can be considered lost. (The relationship of bus to task cycle can be influenced by the user so that the threshold value must be determined individually.) - Subsequent sequences are only permitted to be transmitted in the next bus cycle after the completion check has been carried out successfully. |
The transmit array, which must be created in the program sequence, consists of several elements. The user has to arrange the control and data bytes correctly and transfer the array elements one after the other. The transfer algorithm remains the same and is repeated starting at the point Cyclic checks.
Fig.: Flow chart for the output direction