The input signal is sampled at regular intervals. If the sampling rate used is too low, the input signal will be sampled incorrectly and a flawed image of the oscillation will occur. This undesirable phenomenon is called the aliasing effect.
To avoid such false results, the requirements of the theorem known as Nyquist's sampling theorem must be fulfilled in the sampling. This sampling theorem describes the necessary frequency ratio between the sampling and the signal and states that the sampling rate must be more than double the maximum frequency of the measured signal.
输入信号是以固定的时间间隔进行采样的。如果使用的采样率太低,输入信号将被错误地采样,会出现有缺陷的振荡图像。这种不理想的现象称为混叠效应。
为了避免这种错误的结果,在采样时必须满足被称为奈奎斯特采样定理的要求。这个采样定理描述了采样和信号之间必要的频率比,并指出采样率必须是被测信号最大频率的两倍以上。
Example of incorrect sampling
错误采样示例
Sine wave with 4 kHz sampled at 6kHz. The red wave shows the sine wave measuring 2 kHz, which is a result of the sampling being too low.
4 kHz的正弦波以6kHz采样。红色波表示正弦波测量值为2 kHz,这是采样过低的结果。
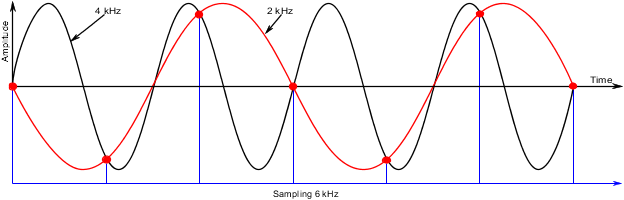
Fig.: Incorrect sampling with 6 kHz and 4 kHz
图: 6 kHz 和 4 kHz 错误采样
Information: 说明: The module ensures that Nyquist's sampling theorem is always fulfilled. With a wanted signal of 10 kHz, a reduced sampling frequency of 25.7812 kHz is used! 该模块确保奈奎斯特采样定理始终得到满足。 对于 10 kHz 的所需信号,则使用降低到 25.7812 kHz 的采样频率! |