Scanning or sampling refers to the recording of an analog value at certain intervals.
At defined times, the precise voltage level of the signal is recorded and stored. The distance Δt (Delta t) between the recording points is called the sampling interval.
扫描或取样是指以一定的时间间隔记录一个模拟值。
在规定的时间,记录并存储信号的精确电压电平。记录点之间的距离Δt(Δt)称为采样间隔。
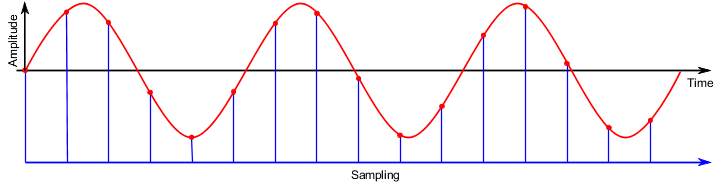
Fig.: Sampling of a curve
图: 曲线的取样
If the actual sampling rate is many times higher than the theoretically required sampling frequency, it is called "oversampling". The reduction of the sampling rate to the required rate is called "downsampling".
If the Fourier transform is used in accordance with the sampling theorem on a purely sinusoidal signal whose frequency corresponds exactly with a node in the frequency spectrum (whole number multiple of the frequency resolution), then this signal appears as a single line in the spectrum. If the frequency of the sinusoidal oscillation does not fall on a node in the frequency spectrum, then it will appear as 2 neighboring lines whose vertical relationship to each other is indirectly proportional to the frequency deviation of the respective node.
In practice, a pure sinusoidal signal will rarely occur. Rather, a signal will consist of a multitude of sinusoidal oscillations of different frequencies. As a result, the resulting frequency spectrum also consists of a large number of lines.
Depending on the resolution selected, the lines manifest themselves in different ways on the spectrum.
如果实际采样率比理论上要求的采样频率高出许多倍,则称为“过采样”。将采样率降低到所需的速率称为“下采样”。
如果根据采样定理对频率与频谱中的节点(频率分辨率的整数倍)精确对应的纯正弦信号使用傅立叶变换,则该信号在频谱中显示为单条线。如果正弦振荡的频率没有落在频谱中的一个节点上,那么它将表现为两条相邻的线,它们彼此的垂直关系间接地与相应节点的频率偏差成比例。
实际上,很少会出现纯正弦信号。相反,信号将由不同频率的大量正弦振荡组成。因此,所得到的频谱也由大量的线组成。
根据所选择的分辨率,这些线在频谱上表现为不同的方式。
Buffer storage Buffer 存储
The values that have been sampled are stored for 300 ms in the module's internal buffer and must be transferred during this time. (See Transferring characteristic values via Flatstream.)
已采样的值在模块的内部缓冲器中存储300ms, 在此期间必须传输。(见 通过Flatstream 传输特征值 。)
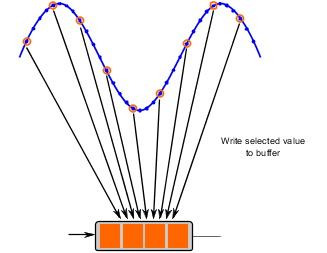
The size of the buffer is constant and can store 8192 measured values. This results in the following relationship between the sampling rate and the duration of measurement.
Measurement duration = Buffer size / Samples per second
Since the number of values stored depends on the configured sampling rate and not the hardware-based sampling rate, not all values that are measured are stored. At a measurement duration of 318 ms, every second value is stored; at a duration of 15.9 ms, every hundredth value is stored.
The number of stored values can be set indirectly through registers MaxFrequencyEnvelope and MaxFrequencyRaw
buffer 的大小是恒定的,可以存储8192个测量值。这就导致了采样率和测量时间之间的关系如下。
测量持续时间 = 缓冲区大小 / 每秒采样数
由于存储的值的数量取决于配置的采样率,而不是基于硬件的采样率,因此并非所有测量的值都会被存储。在 318 毫秒的测量持续时间内,每秒存储一次值;在 15.9 毫秒的持续时间内,几百个值被存储。
存储值的数量可以通过寄存器 MaxFrequencyEnvelope 和 MaxFrequencyRaw间接设置。