Many types of bearing damage are caused by imprecisions in the bearing surface such as material damage or micro-cracks. These pittings (i.e. material damage or micro-cracks) are rolled over by the roller elements cause impacts on the roller bearing and its attachment parts.
许多类型的轴承损坏是由轴承表面精度造成的,如材料损坏或微裂纹。这些凹陷(即材料损坏或微裂纹)被滚动轧过后,会对滚动轴承及其连接部件造成冲击。
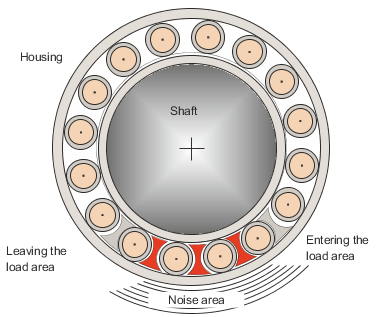
Fig.: Roll-over processes in the bearing
图: 轴承的滚动过程
The mechanism is very similar to the striking of a bell: The clapper strikes the body of the bell, and the bell starts vibrating at its natural frequency.
In the case of the bearing, each time the roller moves over the damaged area it is like the striking of the clapper, and the roller parts and attachment parts start to vibrate.
These very small oscillations can be measured as a modulation or superposition of the excitation frequency on the surface of the bearing.
Appropriate analysis methods such as formation of the envelope can separate the superposition to make the roll-over frequencies of the bearing clearly discernible.
这种机制与敲钟非常相似:拍板敲击钟体,钟开始以其固有频率振动。
在轴承的情况下,每当滚动在损坏的地方移动时,就像拍子敲击一样,滚动部件和附件部件开始振动。
这些非常小的振荡可以作为激励频率在轴承表面的调制或叠加来测量。
适当的分析方法,例如形成包络,可以分离出叠加的频率,使轴承的滚动频率清晰可辨。
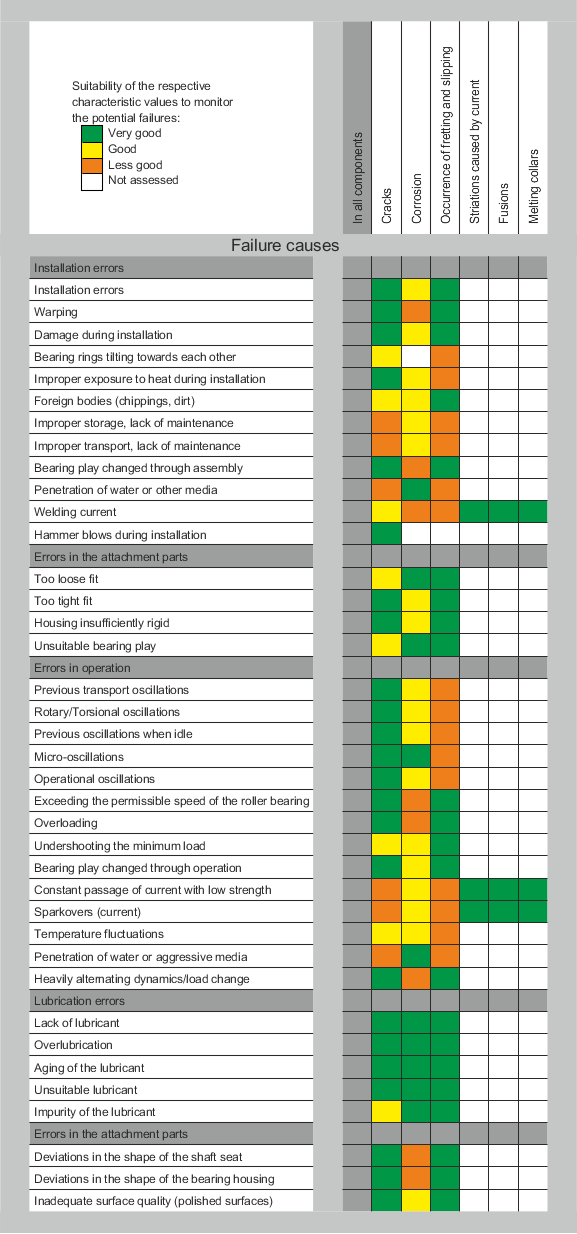
Fig.: Frequency of failure indicators on roller bearings
图: 滚动轴承的故障指标频率
关于各个特征值的含义,见Characteristic values 和 Configuration。
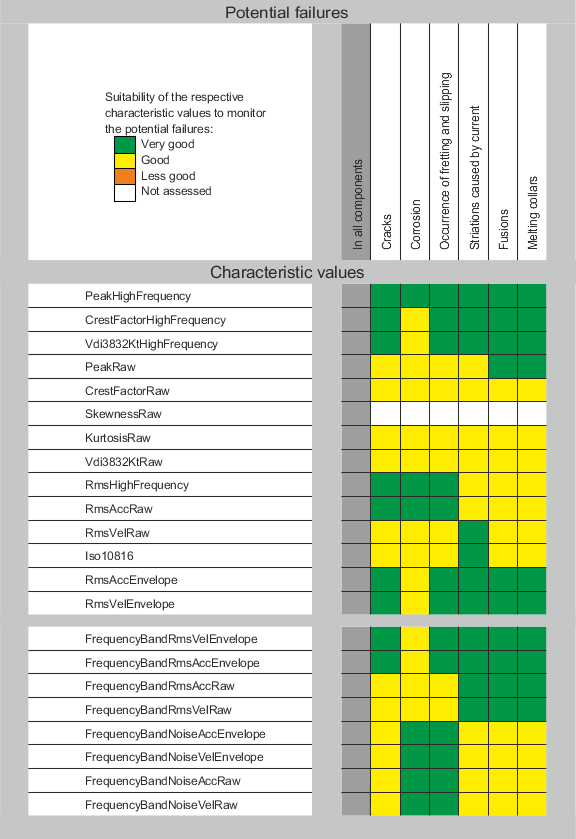
Fig.: Frequency of failure indicators on roller bearings
图: 滚动轴承的故障指标频率
关于各个特征值的含义,见Characteristic values 和 Configuration。