In industrial environments, it is often the case that many different devices from various manufacturers are being used side by side. The electrical and/or electromagnetic properties of these technical devices can sometimes cause them to interfere with one another. These kinds of situations can be reproduced and protected against in laboratory conditions only to a certain point.
Precautions have been taken for X2X Link transfers if this type of interference occurs. For example, if an invalid checksum occurs, the I/O system will ignore the data from this bus cycle and the receiver receives the last valid data once more. With conventional (cyclic) data points, this error can often be ignored. In the following cycle, the same data point is again retrieved, adjusted and transferred.
Using Forward functionality with Flatstream communication makes this situation more complex. The receiver receives the old data again in this situation as well, i.e. the previous values for SequenceAck/SequenceCounter and the old MTU.
在工业环境中,通常会同时使用来自不同制造商的许多不同设备。这些技术设备的电气和/或电磁特性有时会导致它们相互干扰。这类情况在实验室条件下只能在一定程度上得到重现和防护。
如果发生此类干扰,X2X链路传输已经采取了预防措施。例如,如果出现无效的校验和,I/O系统将忽略这个总线周期中的数据,并且接收端再次接收最后一个有效的数据。对于传统的(周期性)数据点,这种错误往往可以被忽略。在下一个周期,同样的数据点会再次被检索、调整和传输。
使用Flat流通信的 Forward 功能使这种情况更加复杂。在这种情况下,接收端也会再次收到旧的数据,即SequenceAck/SequenceCounter的先前值和旧的MTU。
Loss of acknowledgment (SequenceAck)
确认丢失(SequenceAck)
If a SequenceAck value is lost, then the MTU was already transferred properly. For this reason, the receiver is permitted to continue processing with the next sequence. The SequenceAck is aligned with the associated SequenceCounter and sent back to the transmitter. Checking the incoming acknowledgments shows that all sequences up to the last one acknowledged have been transferred successfully (see sequences 1 and 2 in the image).
如果一个SequenceAck值丢失,则表明MTU已正确传输。出于这个原因,允许接收方继续处理下一个序列。SequenceAck与相关的SequenceCounter对齐,并发回给发送端。检查传入的确认消息的标志,直到最后一个确认的序列为止的所有序列都已成功传输(见图片中的序列1和2)。
Loss of transmission (SequenceCounter, MTU):
传输丢失(SequenceCounter,MTU):
If a bus cycle drops out and causes the value of SequenceCounter and/or the filled MTU to be lost, then no data reaches the receiver. At this point, the transmission routine is not yet affected by the error. The time-controlled MTU is released again and can be rewritten to.
The receiver receives SequenceCounter values that have been incremented several times. For the receive array to be put together correctly, the receiver is only permitted to process transmissions whose SequenceCounter has been increased by one. The incoming sequences must be ignored, i.e. the receiver stops and no longer transmits back any acknowledgments.
If the maximum number of unacknowledged sequences has been sent and no acknowledgments are returned, the transmitter must repeat the affected SequenceCounter and associated MTUs (see sequence 3 and 4 in the image).
如果总线周期中断并导致SequenceCounter的值和/或填充的MTU丢失,则没有数据到达接收端。此时,传输程序还没有受到错误的影响。时间控制的MTU再次被释放,可以被重写
接收端收到的SequenceCounter值已经被多次递增。为了使接收数组正确地组合起来,接收端只允许处理SequenceCounter被增加了1的传输。传入的序列必须被忽略,也就是说,接收端停止并不再传送回任何确认。
如果已经发送了最大数量的未确认序列,并且没有返回确认,发射端必须重复受影响的SequenceCounter和相关MTU(见图片中的序列3和4)。
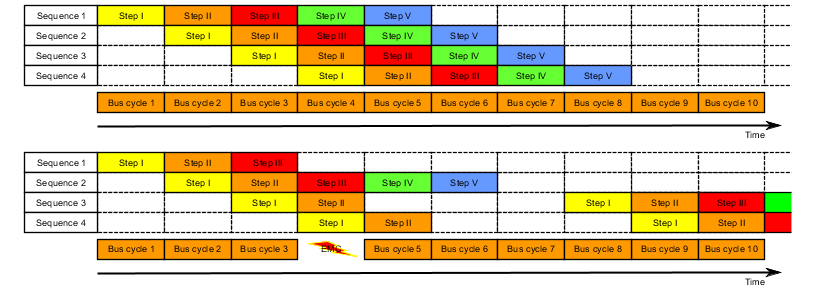
Fig.: Effect of a lost bus cycle
图: 丢失总线周期的影响
Loss of acknowledgment
确认信息丢失
In sequence 1, the acknowledgment is lost due to disturbance. Sequences 1 and 2 are therefore acknowledged in Step V of sequence 2.
在序列1中,由于干扰,确认被丢失。因此,在序列2的步骤V中确认序列1和2。
Loss of transmission
传输丢失
In sequence 3, the entire transmission is lost due to disturbance. The receiver stops and no longer sends back any acknowledgments.
The transmitting station continues transmitting until it has issued the maximum permissible number of unacknowledged transmissions.
5 bus cycles later at the earliest (depending on the configuration), it begins resending the unsuccessfully sent transmissions.
在序列3中,整个传输由于干扰而丢失。接收端停止并且不再发回任何确认。
发送端继续发送,直到它发出了最大允许数量的未确认的传输。
最早在5个总线周期后(取决于配置),它开始重新发送未成功发送的传输。